What Are You Looking For?
What are the hydrogen storage technologies? (I) - Physically based storage (gas or liquid)
Hydrogen storage methods used by industry and academia can be divided into two types:
Physics-based storage (gaseous or liquid)
Materials-based storage (hydrogen interacting with storage materials)
In physics-based storage, two main storage methods are commonly used; they are gaseous and liquid hydrogen storage.
1.1 Gaseous hydrogen storage
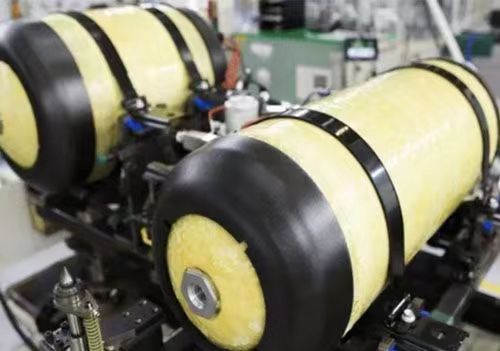
Gaseous storage involves pressurizing hydrogen and storing it in gas form in specific containers. Depending on the pressure, gaseous storage can be divided into low-pressure storage and high-pressure storage.Hydrogen can be stored at low pressure like natural gas, using water-sealed tanks. This method is suitable for large-scale gas storage. Since the density of hydrogen is low, it has few applications. Gaseous high-pressure storage is a common and direct storage method. Hydrogen can be released directly through the adjustment of a high-pressure valve. Nominal high-pressure gaseous hydrogen storage is a widely used, simple and easy hydrogen storage method. The charging and releasing speed is fast and can be carried out at nominal temperature. However, its disadvantages are that it requires a heavy pressure-resistant container, consumes a large amount of hydrogen compression work, and has unsafe factors such as easy leakage of hydrogen and explosion of the container.
Gaseous storage places high demands on gas tanks. Currently, hydrogen storage tanks (350 bar and 700 bar) composed of type IV carbon fiber are widely used in vehicles. In order to withstand such high pressures, the tank material should be very strong, and compressing hydrogen to such high pressures requires complicated compression work, the cost is very high.
This compressed gas storage method is not only used for vehicles transported by road, but also for stationary applications in gas stations for the distribution of hydrogen and stationary power generation.
1.2 Liquid hydrogen storage
At a certain low temperature, hydrogen will exist in liquid form. Therefore, a cryogenic liquid hydrogen storage technology can be used - cryogenic liquid hydrogen storage. Similar to air liquefaction, low temperature liquid hydrogen storage is first compressed hydrogen, before passing through the throttle valve to cool, undergo Joule-Thomson isothermal enthalpy expansion to produce some liquid. After the liquid is separated, it is stored in an insulated vessel with high vacuum, and the gas continues the above cycle.
Liquid hydrogen storage has high volumetric energy density, the density of liquid hydrogen at normal temperature and pressure is 845 times that of gaseous hydrogen, and the volumetric energy density is several times higher than that of compressed storage. Compared with hydrogen storage containers of the same volume, the hydrogen storage quality is greatly improved. The liquid hydrogen storage technology is particularly suitable for transportation situations with limited storage space, such as rocket engines for space shuttles, automobile engines, and intercontinental flight transportation vehicles. If only considered in terms of mass and volume, liquid hydrogen storage is an extremely ideal way to store hydrogen. However, since hydrogen liquefaction requires a large amount of cooling energy, liquefying 1kg of hydrogen requires 4-10kWh of electricity, which increases the cost of hydrogen storage and use. In addition, liquid hydrogen storage containers must use ultra-low temperature special containers. temperature. Since the filling and insulation of liquid hydrogen storage can easily lead to higher evaporation losses, the storage cost is more expensive and the safety technology is more complicated. Highly insulated hydrogen storage containers are the focus of current research.
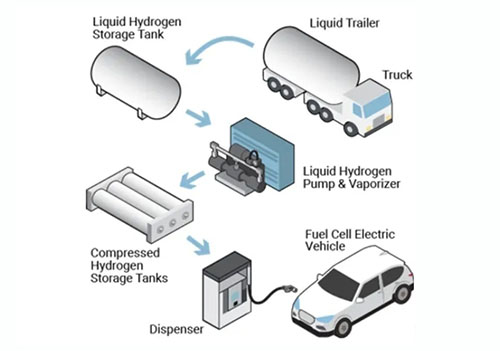
1.3 Freezing and compressing storage
Freeze and compress storage use the properties of liquid and compressed gaseous hydrogen methods for hydrogen storage.This technology can reduce the evaporation rate of hydrogen and completely maintain high energy density. Compression tanks typically store hydrogen at a temperature of -253°C and a high pressure of approximately 300 bar.