High-performance Gore Proton Exchange Membrane, helping to reduce the cost of all "Hydrogen".
In hydrogen demonstration city clusters such as Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and the Yangtze River Delta, a large number of hydrogen vehicles have been put into daily logistics transportation. Up to now, the ownership of heavy trucks like hydrogen has exceeded 3,000 units in China. Along with the trend of hydrogen energy development, experts expect that the cost of hydrogen-fueled vehicles is expected to drop significantly in 2025, and realize the application and promotion in more regions.
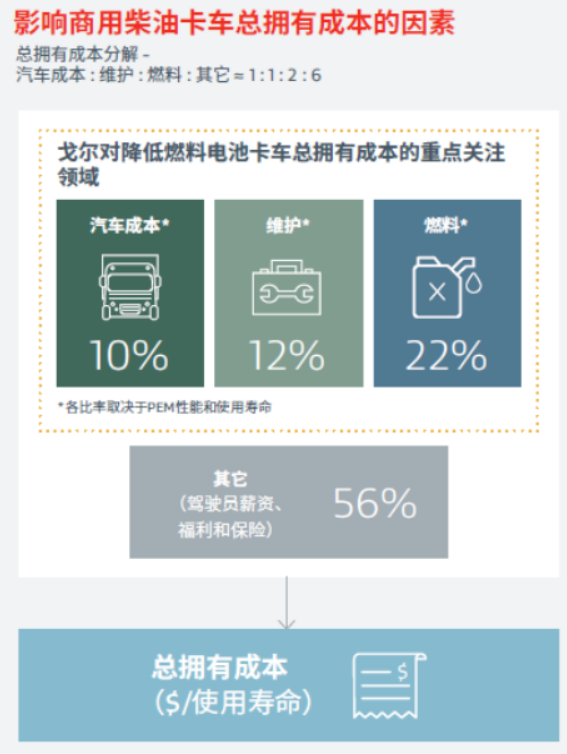
In order to respond to and accelerate the commercialization of hydrogen-fueled vehicles, solving the "choke point" cost issue is a central key. Shinichi Nishimura, Global Product Specialist for Fuel Cell Technology at W. L. Gore & Associates, points out that vehicle, fuel and maintenance costs account for 44% of the total cost of ownership of a conventional diesel truck. Throughout the upstream and downstream, how to solve the cost problem from the whole chain, so that the cost of hydrogen fuel cell is equal to the traditional fuel solution has become the focus of Gore.
As the developer of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE), Gore has been actively engaged in this field for many years. Based on its "ever-changing" structural properties, Gore has further developed GORE-SELECT® proton exchange membranes with excellent performance, which can effectively reduce the total cost of ownership of the fuel cell by improving fuel efficiency and optimizing the design of the cell system. By improving fuel efficiency and optimizing the design of the battery system, the total cost of ownership of fuel cells can be effectively reduced, which will contribute to the large-scale application of hydrogen commercial vehicles.

Gore's two-pronged approach empowers cost optimization across the fuel cell value chain
Improved fuel efficiency
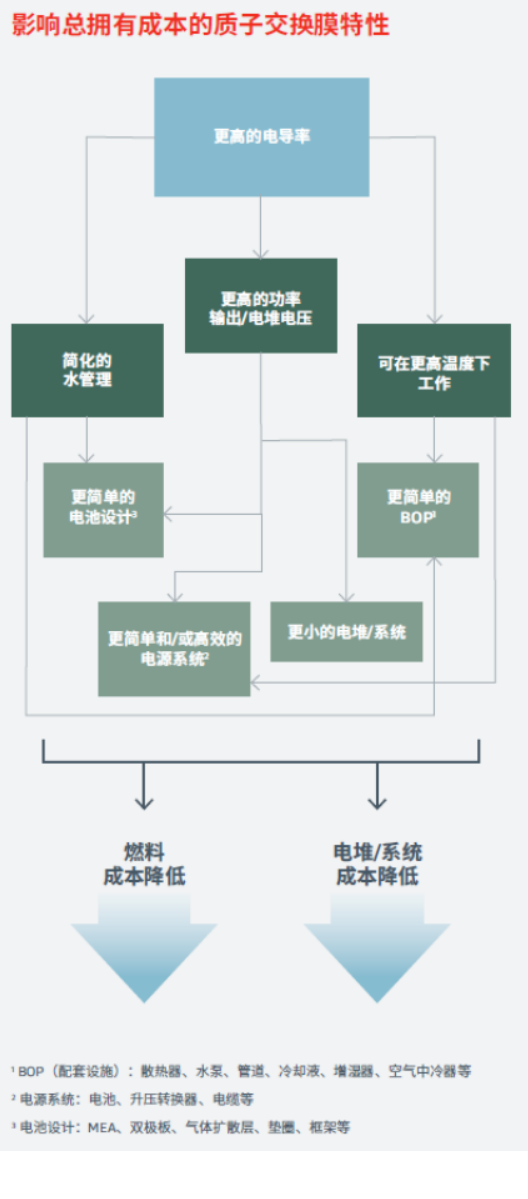
The rigorously tested GORE-SELECT® proton exchange membrane has higher conductivity and lower gas permeability, which on one hand can help commercial fuel cell vehicles operate at higher temperatures, thus improving fuel efficiency. On the other hand, it can help manufacturers to make radiators from existing components, or even smaller radiators using less material, thus reducing automotive manufacturing costs.
Optimized system design
The high cost of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is also due to the complexity of the components in the system. The modified GORE-SELECT® Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) reduces membrane thickness, simplifying BOP and cell design and lowering fuel cell system costs. By enabling excellent water management, the PEM can operate at low relative humidity (RH) and high operating temperatures, which means that the configuration of external humidifiers can be eliminated or humidifiers can be downsized. It can be said that the optimization of Gore's PEM membrane thickness not only results in lower fuel cell system costs, but also eliminates the need for frequent and complex maintenance (lowering maintenance costs), and truly reduces the total cost of ownership from the entire value chain.
In the coming years, hydrogen energy will be used in more commercial vehicles, as well as in more categories and segments. Based on decades of proven market experience and leading-edge materials technology, Gore is able to analyze fuel cell system requirements and adapt materials to continue to provide better-suited, more attractive solutions for hydrogen-powered commercial vehicles, helping manufacturers achieve faster total cost of ownership reductions and accelerating the global shift to clean energy.